How precision agriculture helps increase productivity
Bananas are the world’s favorite fruit. They are the most commonly traded fruit and the fifth most traded agricultural product. Worldwide banana exports totaled an estimated US$13.6 billion in 20181.

There are over a thousand different varieties of bananas growing around the world. Some are sweet, like the Cavendish banana, which is the most common and widely exported variety, accounting for half the bananas on supermarket shelves.
But monocropping comes with risks, and the ubiquitous banana is under threat. Currently, a new outbreak of Panama disease caused by the strain Tropical Race 4 (TR4) threatens the production of today's most popular banana, Cavendish.
What’s the worst that could happen? The collapse of the Big Mike banana
The world has weathered banana pandemics in the past. Until the 1950s, the dominant banana variety was the Big Mike (Gros Michel). It was grown in a similar way to today’s Cavendish: monocropped over large areas. Over time, monocropping reduces soil quality, leaving plants more vulnerable to infection.
The Big Mike was uniquely susceptible to Panama disease (Fusarium wilt), which devastated the variety - and the livelihoods of the farmers who grew it. Between 1940 and 1960, 30,000 hectares of a plantation in the Ulua Valley of Honduras were completely destroyed3 - a story, which was repeated again and again around the world, and without rapid action, it could be seen again with the Cavendish banana.
Stressed crops = reduced production
Latin America and the Caribbean constitute the world’s most important exporting region for bananas, playing a vital role in the global fruit supply.
In Mexico, the highest production is found in the south-southeast region of the country, which has the right climate, a great amount of water and the right land properties for banana production. The region is difficult to access - especially compared to other regions that grow bananas - as the area is remote and rugged.
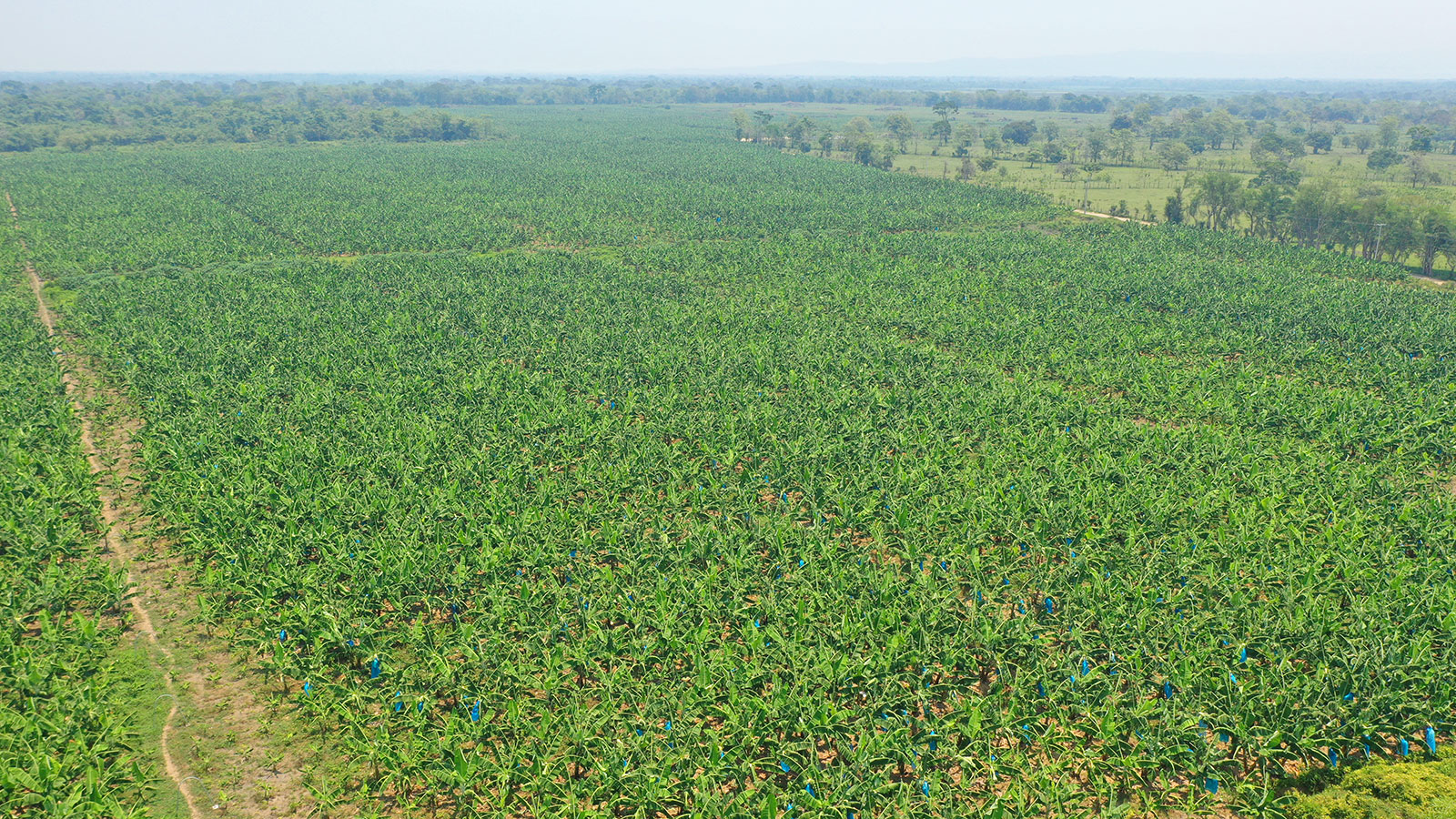

“If it’s difficult to access crops, there is a bigger chance of missing an issue in the initial stages where preventive actions can still be made. Using drones for scouting and software for crop analysis makes the monitoring workflow more efficient and easier,” says Álvaro Ruiz, COO, CoatzaDrone.
Additionally, in banana production, the main concern is if the plant gets stressed due to a lack of water. The fruit quality decreases with greater stress, resulting in a decrease in sugar content (measured by degrees Brix).
What is the Brix fruit level?
Degrees Brix, usually shortened to "Brix", is a scale of measurement for soluble solids in a liquid. In the juices of fruits and vegetables, soluble solids are mostly sugars, and the Brix measurement approximates the sugar content of a sample. A higher Brix level means higher sugar and a better flavor. Bananas will be at their best, in terms of sweetness, when they reach 16 degrees Brix.
Another problem with banana cultivation is the type of soil. Bananas are typically grown in wetland gleysol, characterized by clayey texture and excess humidity. Along with high temperatures, these conditions promote pathogen generation (both fungi and bacteria). Diseases like Black Sigatoka, together with this specific soil type can cause a decrease in the leaf area and a resulting reduction of active photosynthetic area. This affects the number of flowers, number, and weight of hands (banana clusters), resulting in the product reduction overall.
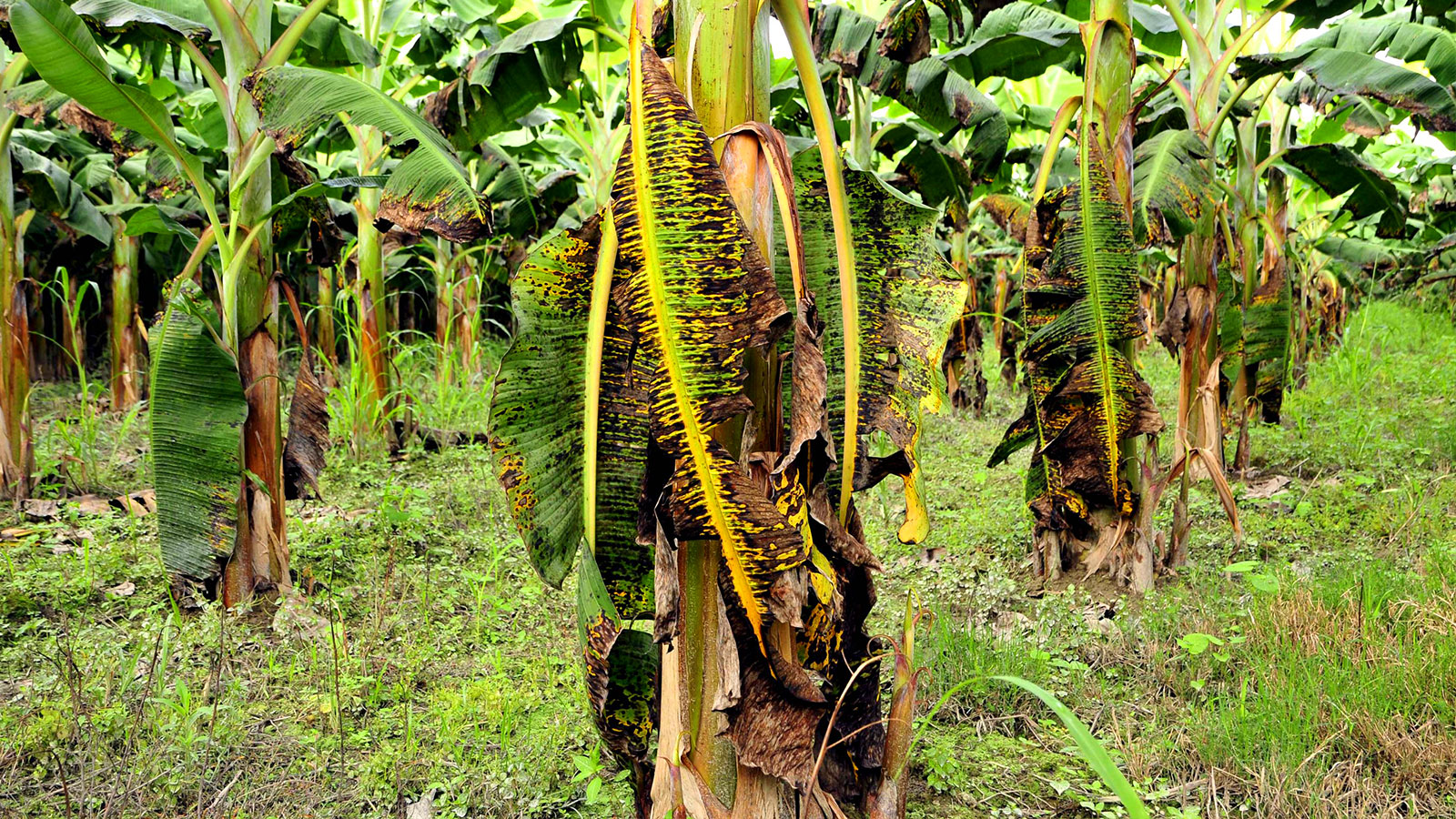

For the fruit to be suitable for export, crop-specific criteria need to be met.
The usual solution is to increase the inputs like water and nutrients - all of which come at a cost. CoatzaDrone and Advan México turned to drone mapping and implemented precision agriculture techniques to improve banana production, with a lower price tag.
Monitoring banana crops with precision agriculture
“With the maps created in Pix4Dfields, we can also identify the places where these problems occur and make targeted decisions to level or make drains, or apply more fungicide or pesticide,” says Esteban Chavez Cocom, Agronomist Engineer, Advan México.
Project details: saving the world’s favorite fruit
| Location | Teapa, Tabasco, México |
| Companies | CoatzaDrone Advan México |
| Hardware | DJI Phantom 4 Pro Parrot Sequoia camera |
| Software | Pix4Dfields |
| Images | 1,770 multispectral 885 RGB |
| Area | 20.6 ha |
| Processing time | <30 minutes |
| Outputs | Orthomosaic, index map |
| Flight height | 60 meters |
| Flight time | 35 mins approx 2 flights |
| Image size | RGB: 1.4 cm/pix Multispectral: 5.6 cm/pix |

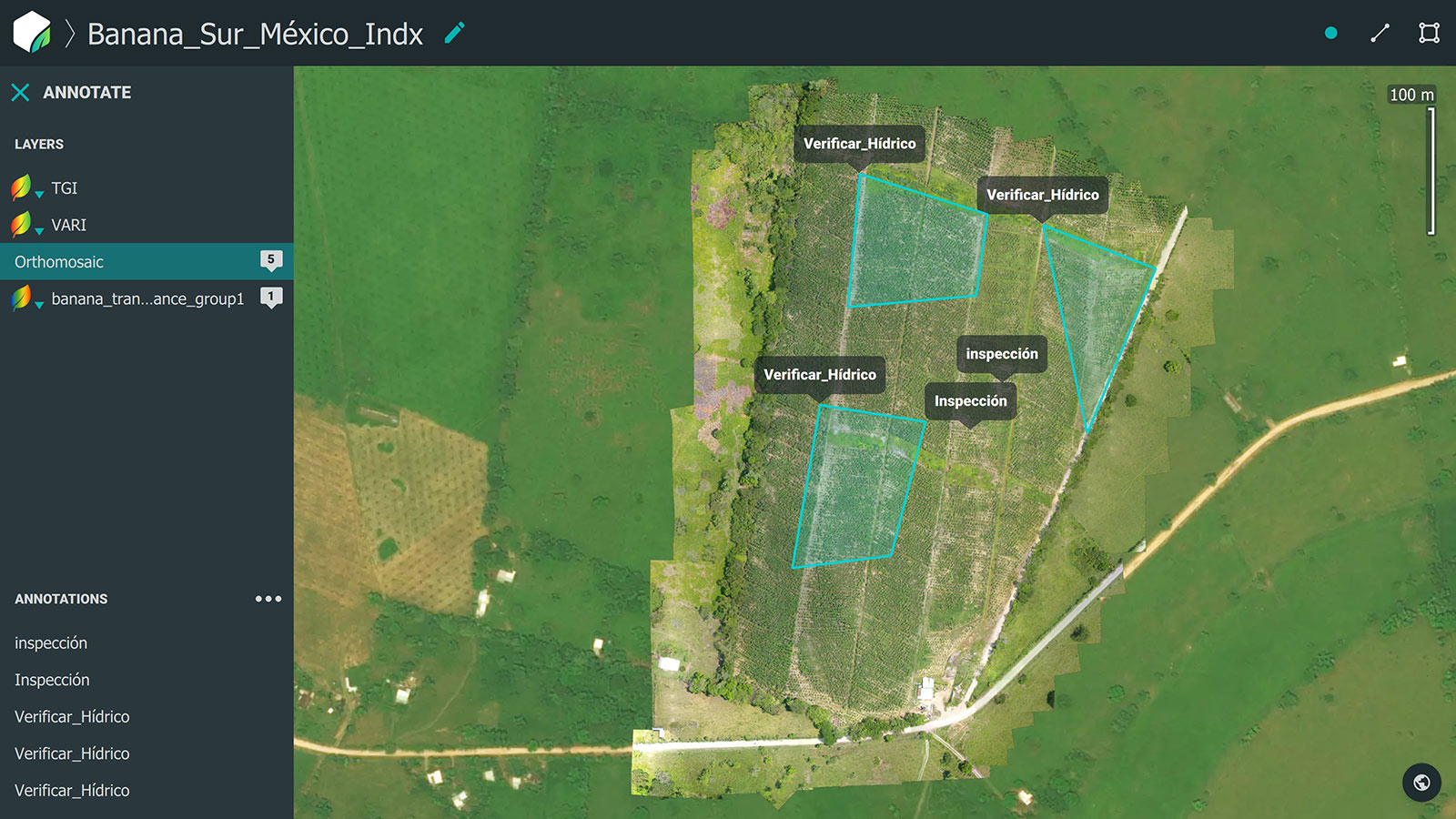
Images were processed in Pix4Dfields to create an aerial representation of banana crops - orthomosaic, and index maps to highlight problem areas even more. Between time needed to fly the drone and collect the data, process the images, generate the maps and interpret them, CoatzaDrone and Advan México were able to deliver results in less than 24 hours.
In the areas marked on the map, we can see a lower population of bananas due to waterlogging, as well as plants that did not reach their full potential size due to the lack of water. Bananas in those areas are reduced in size (deficit of 15-20% of the required length) and the Brix fruit level is lower due to the lack of photosynthesis.
Improving crop production by 30%
CoatzaDrone and Advan México were able to identify the points of greatest water stress and take targeted action by using precision agriculture techniques.
Installing irrigation or digging drains, as the site requires has the potential to improve not only this crop but the seasons to come.
“By knowing where to turn on the irrigation in a targeted way, considerably saved the use of water, energy, and costs. Having good practices for the identification of probable areas of water stress and applying the necessary corrective measures in these areas, it is expected we will be able to improve production by 30% annually,” concludes Esteban Chavez Cocom.
References
| 1"Banana market review, FAO", Back to top 2 "Is a banana a fruit or a herb", Back to article 3"Panama disease", Back to article |